
How to Incorporate Design Principles into Your Projects

Andrea Hill
December 19, 2019
In our last blog post, we talked about experimentation. As fellows at the Next Generation (NextGen) Travel Program at Public Services and Procurement Canada (PSPC), that’s exactly the mandate. Our host team is “re-imagining the government travel experience,” and we’re supporting them by listening to users, digging deep into the rules and policies that govern business travel, and iterating on solutions to improve the experience.
As you can imagine, we’ve had a lot of ideas on how we could improve things. But often, there’s a huge gap between the product or service that someone has in mind, and how it actually ends up when it’s launched. And when we design something, we bring our own experiences, biases and perceptions into the work. It’s just human nature. We can’t avoid that; but we can mitigate the risk by working in a user-centric fashion.
We don’t just mean we work with the user in mind. Instead, we’ve been building tangible examples of our ideas, and bringing them to users to gauge their response. We know we’re not going to get everything right the first time, so we want to get feedback early and often so we can refine our work.
In other words, we’ve pushed beyond the ‘thinking’ part of design thinking, and now we’re prototyping.
Very early on in our fellowship, it became apparent that “prototype” means something very different in the startup/software space than it does in the public sector.
From our perspective, a prototype is simply a quick way to test a hypothesis. It can take the form of drawings on paper, a clickable series of screens, or even a call script for customer support reps.
When we show users a prototype, it’s not a promise to deliver. It’s a test to help inform whether we should deliver “something like this”. When we put time and effort into creating and testing a prototype, the value isn’t in the artefact itself. It’s in the ability to learn quickly.
In contrast, showing something tangible in the public sector can be seen as a sign that a decision has been made, a lot of development has taken place or a direction has been chosen.
“Prototyping allows us to learn before we commit to buying or building something.”
Because we’re trying to learn as quickly as possible, sometimes prototypes are pretty unpolished. They may not adhere to certain brand or security standards. They may include placeholder data, or not even have any backend services at all.
My favourite example? The founder of the successful online shoe company Zappos wasn’t sure if people would be willing to buy shoes online. He didn’t waste time (and money) building an inventory: first he put up a website to see if anyone would buy. When people did buy from his site, he walked into his local shoe store, bought the shoes, and mailed them to the customers. He was able to learn quickly that the idea was a good one, and only then did he invest more heavily in the infrastructure necessary.
In short, prototyping allows us to learn before we commit to buying or building something (and then maintaining and supporting that thing down the road).

Prototypes are a way to explore options in an inexpensive way, so we can feel confident in our investments.
Best-selling author of “Lean Startup” and “The Startup Way” Eric Ries writes, “In today’s marketplace of uncertainty, whoever learns fastest wins.” He was talking about a competitive market, but it holds doubly sure for public services. If something is unusable or doesn’t meet the needs of a country’s residents, it’s much better to discover this in the early design phase, rather than after months or years of development. Trying to change a service once it’s been developed and released is difficult, expensive, and risks eroding the confidence of your customers. Working with users throughout the design and development stages can help identify and address issues, concerns and problems before major decisions are made.
There are many different risks to surmount when delivering products and services. We often classify them into three buckets:
What we’re trying to learn shapes the questions we ask, and those questions in turn shape the kind of prototype we build.
A lot of the work we’ve been doing with the NextGen Travel team is concept testing. This is about putting a high-level concept in front of users and getting their reactions. When we present this concept, do they understand it? Do they recognize it as an attractive solution to their problem?
Public servants are responsible for adhering to policies and guidelines when booking travel. One thing we heard from users was booking travel can be a difficult and complicated process to understand. So we came up with a concept for a “policy guidebook” that would consolidate travel information, provide direct links to relevant policies, as well as a description of “how it’s applied in your department” in plain language.
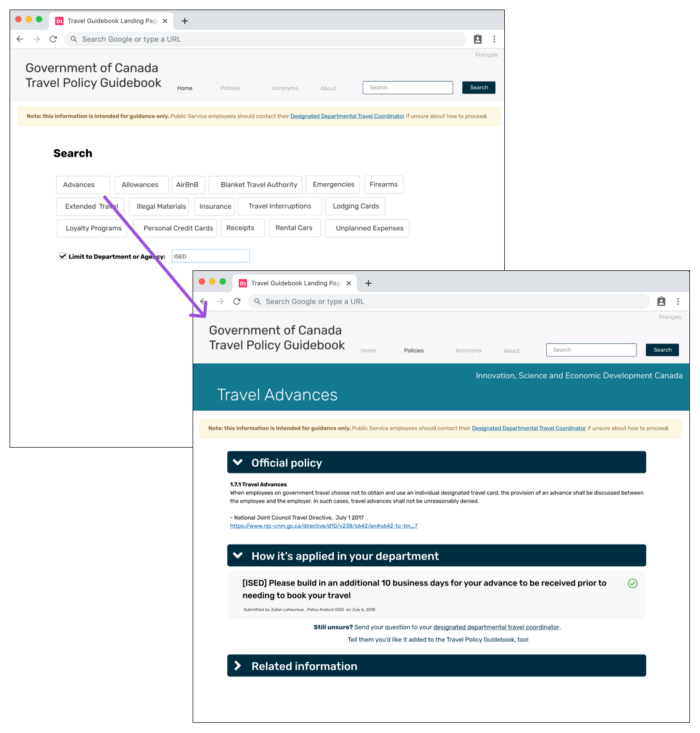
Within two weeks of coming up with this idea, we were able to put a clickable prototype in front of users to get feedback. The functionality of the prototype was pretty limited: only the first page and the “Advances” page were built out.
The point was to get feedback on the general concept, so we didn’t spend excess time building out all the content — nor did we develop it in code. When we met with users, we explained that this was a concept, not everything worked and directed them down the path to explore that page.
What did we learn? Discovering policies and guidelines around travel is definitely an issue, but this way of surfacing them wasn’t intuitive. Less experienced travellers wanted something to walk them through the whole travel process, and surface policies at the moment they were applicable.
At this point, we gave up on this “policy lookup” concept and didn’t put any more effort into the prototype. It had served its purpose as a vehicle for learning, and so we moved on.
Proofs of concept are generally undertaken by more technical teammates, when the question to address is “is this technically possible”?
This type of prototyping may not seem as glitzy or flashy as prototypes that are geared towards the end-user, but they’re critical to project success! There’s no benefit to finding out that your users really want a virtual reality immersive travel tool if you can’t deliver on it.
We’ve probably all been through a procurement or outsourced project where unclear technical requirements blew out the scope or functionality of the product way too late. Prototyping proofs of concept early on helps avoid more expensive mistakes later. It can also help identify other opportunities once we have a clear understanding of the data we can access programmatically.
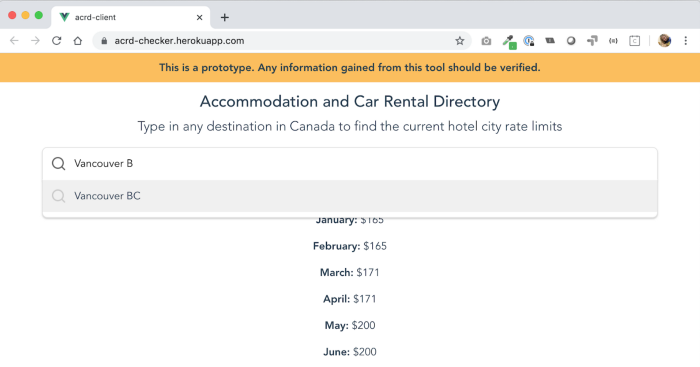
Currently, public servants have to go to a webpage for car rental and accommodations rates, scroll down to the city they’re travelling to, and look up the maximum daily hotel rate for that city based on time of year.
Mike wanted to know whether it was possible to capture and display that content in a more user-friendly format. He created a web scraper that read the content from the webpage. Then he built a simple interface that let the user select a city and a date, and then be provided with the correct rate.
This wasn’t intended to be a standalone tool for travellers, but it proved that the feature was feasible and could be integrated into other products or services as a way to add value to users.
Once we’re confident that we’re addressing a real problem and the high level concept makes sense, we can move onto usability testing.
While we want the prototype to be as close as possible to the final product, that doesn’t mean that it all needs to be “working.” I know of a team who was conducting usability testing on their content: they wanted to know if labels and messaging were straightforward. So they printed the messaging on index cards rather than put the time into building a website or clickable prototype.
If you’re working on a more interactive or complicated web application, it’s advisable to build a more robust prototype. It creates more avenues for learning; and people will always surprise you when you put something in front of them! This is not the time to be complacent with “sure, looks good”-style responses.
Once Mike determined that he could access the city rate limits programmatically (as mentioned above), we created a prototype for a cost estimator. When a prospective traveller wants to create a cost estimate for a trip, they can go to this site. They can type in the city they’re travelling to, the dates, and the cost estimates are calculated automatically.
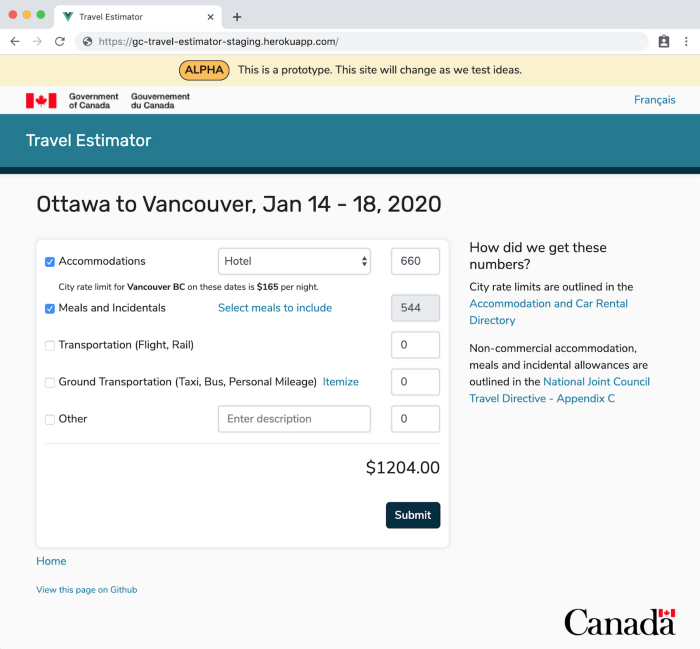
Through the process of asking public servants to try out our cost estimator prototype, we’ve been able to refine the design and functionality. Initially we had only displayed the total allowable amount for the entire hotel stay. But seeing users’ confusion led us to iterate, improve the prototype and add more explanatory text that provided them the daily rate as well as the total.
As we’ve developed and tested prototypes through our fellowship, we’ve achieved a few goals. We’ve been able to test our assumptions and now have more confidence that we’re designing a travel solution that meets the needs of public servants. We’ve also been able to promote and encourage a new way of working. We’ve been able to show our government partners how a glimmer of an idea can be rendered into an artefact that others can respond to.
“The most rewarding prototypes can be the ones where you realize your ideas were headed down the wrong path, and you can switch course before you’ve made too much of an investment.”
Ultimately, the value of this way of working isn’t the artefact that is created. It’s the process of prototyping that matters most: investing a small amount of resources to try something, learn from it, recalibrate and try again. In other words, it’s best to think about prototype as a verb, not just a noun.
When we leave the public service in March, whether the prototypes live on or not, it’s the learnings they elicited that will help inform the future of government travel.
Hopefully, this post has convinced you of the benefit of prototyping: the ability to learn from users early on, so you can feel more confident you’re working on a solution that’ll be desirable, viable and feasible.
It’s also fun! You get to be creative, without the pressure of having to be right all the time. The most rewarding prototypes can be the ones where you realize your ideas were headed down the wrong path, and you can switch course before you’ve made too much of an investment.
So I invite you to give prototyping a try on your next project. Don’t just rush to the first solution that comes to mind. Do a quick mockup — this could be on the back of a napkin, a flowchart or an interactive prototype — and put it in front of the user. Ask them to critique it, and surface blindspots or new opportunities early on.
And if you have any specific questions about prototyping, running user tests, or anything else about user-centred design, please, reach out!
End of articles list